Force:- A push or a pull on an object is called force.
SI unit of Force – Newton (N)
C.G.S. unit of force – Dyne
1Newtom =105Dyne

Direction of the force: - The direction of the push or the pull on an object is called direction of the force.
|
|
|
On an object at rest:- A force can move an object at rest.
Ex:- If a force is applied on a book the book can move in the direction of force.
On a moving object:- A force can have following effects on a moving object.
On Shape:- Force can change the shape of an object.

Figure 5 Force can change the shape of an object
There are two main types of forces contact force and non-contact force.
| Contact forces | Non-contact forces |
| These kinds of forces are applied only when two or more objects come in contact with each other. | These kinds of forces are applied when the objects do not come in contact with each other and yet are exerting a force upon each other. |
| Ex: Muscular Force, Frictional Force | Ex: Magnetic Force, Gravitational Force, Electrostatic Force |
(a)Muscular Force:- The force that is exerted by the muscles of our body or living organism is called muscular force.
OR The force that comes into play because of the action of muscles is called muscular force.
EX- A bullock, horse, camel is able to pull a cart because of muscular force.
* Human beings use muscular force in order to walk.
* The expansion and contraction of lungs is because of muscular force.
* Movement of food along the food pipe
* Animals can also exit muscular forces; that's why they can move from one place to another

Figure 6 Muscular Force applied in Tug-of-War

Figure 7 Muscular Force applied by Animals
(b) Friction:- When one surface is moving over another surface, a force comes into play and opposes their relative motion. This force is called friction or force of friction.
Ex:- A ball rolling along the ground stops after sometime due to friction.
Stop pedalling a bicycle,it gradually slows down and finally come to stop.


(b) Electrostatic Force: - The force which applied by a charged body on another charged or non-charged body are called electrostatic force.
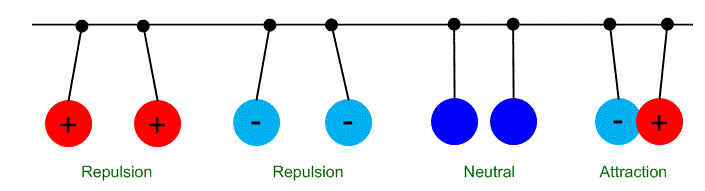
(c) Gravitational Force: - The force by which all objects attract each other is called gravitational force.
Or, The attractive force between two objects that have mass is called gravitational force/force of gravity/gravity.
It is an attractive force that is applied by the earth on all the objects.
It is also called the force of gravity or gravity that acts upon all the objects that are present on or near the Earth's surface.
Gravity is a property exhibited by every object present in the universe and not only the earth. Hence, all the planets, the moons and even the sun have a gravitational force of their own.

QUE: Are weight and mass the same thing?
Ans:- Weight and mass are not the same. Mass is the amount of matter contained in an object, usually measured in kilograms. Weight is a force that depends on mass and gravity, usually measured in newton (N).
Pressure = force/area

Following examples are related to pressure:
A needle has a pointed end that has a very small surface area. Hence when a large force is exerted upon the needle with a hammer the pressure on the needle increases and it easily moves inside the wall.
Shoulder bags always have broad straps rather than thin straps in order to minimize the pressure that would be exerted on the shoulders of the career due to the gravitational force acting upon the bag.
Tools that are used for cutting and piercing always have sharp edges because as a person would apply a force on the tool, its sharp edges would exert more pressure due to less surface area and the object wood cut down easily.
The two tyres of a tractor are wider because it minimizes the pressure exerted by the tractor on the ground. As a result, it becomes easier to move the tractor on a muddy field.
Camel can walk easily over the sand because it has wide feet which allow them to walk on sand easily. Human beings, on the other hand, cannot as walk easily on sand as their feet have less surface area and therefore our feet sink in the sand.
Unit of Pressure:-
Q 1.A force of 20 N acts over a surface having an area of 4 m2 .What is the pressure on this surface.
Sol:- Given, force = 20 N ; Area = 4 m2 ; pressure = ?
We know that pressure = force/area = 20/4 = 5 N/m2
Q 2. A pressure of 50 N/m2acts on the area of 5 m2 .Calculate the total force acting on the given area.
Sol:- Given, pressure =50 N/m2 ; area = 5 m2 ; force = ?
We know that pressure = force/area or Force = pressure × area = 50 × 5 = 250 N
Q 3. A force of 800 N exerts a pressure of 40 N/m2 . What area is it acting on?
Sol:- Given, pressure = 40 N/m2 ; Force = 40 N/m2 ; area = ?
We know that pressure = force/area or area = force/pressure = 800/40 = 20 m2
Q 4. A person weight 600 N. He is wearing shoes with a total area of 0.02m2 . What pressure do they exert on the floor?
Sol:- Given, force = 600 N ; area = 0.02m2 ; pressure = ?
We know that pressure = force/area = 600/0.02 = 30000 N/m2
Liquids and gases exert pressure as follows:
Atmosphere:-The layer of air around us is called atmosphere.
Atmospheric Pressure:-The pressure exerted by atmospheric air is called atmospheric pressure.
* The weight of air in a column of height of atmosphere and area 10 x 10 cm is 1000 kg. This is roughly same as the area of our head. That is you have 1000 kg of air on your head.
Note :-Manometer is used to measure pressure. A barometer is used to measure the atmospheric pressure.